ESTROGEN DOMINANCE
Estrogen—no woman should take additional supplements. We already have over 100 estrogen mimics present in our environment. Additionally, men can also experience symptoms of estrogen dominance.
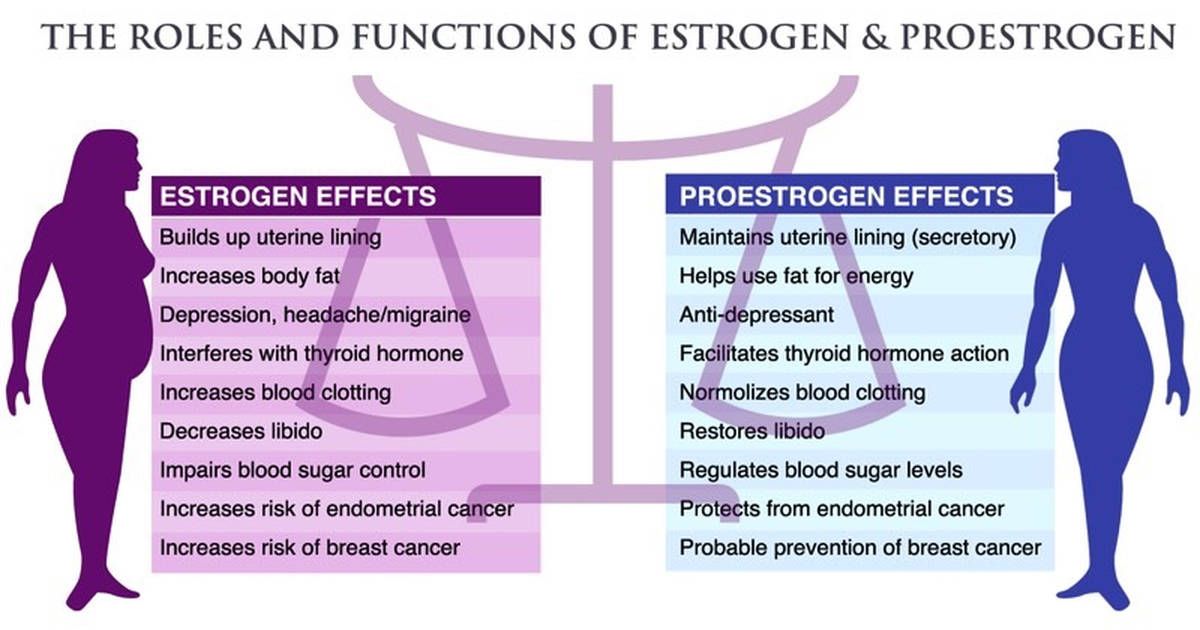
Estrogen Dominance, affectionately dubbed the 'monster,' certainly lives up to its name! This term is frequently used to characterize the negative symptoms experienced by both men and women when they possess elevated levels of estrogen. For women, this often occurs due to prolonged use of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) and Contraceptives, resulting in diminished progesterone levels.
Initially, progesterone exerts a stimulating effect. This occurs because progesterone activates estrogen receptors, allowing estrogen to take precedence as the dominant hormone, which can lead to many men and women feeling worse.
Progesterone gradually establishes itself as the primary hormone, leading to a reduction in symptoms. Some women may never encounter estrogen dominance, while others may see its effects after several days, and for some, it may persist for a longer duration. The duration largely depends on the level of excess estrogen present.
Men can also experience estrogen dominance when first using progesterone.
When beginning progesterone therapy, it's crucial to administer an adequate dosage of approximately 200-400 mg per day or 6-12 ml daily to effectively counteract excess estrogen. A common misconception is that a lower dose of 20-40 mg per day will suffice; however, this is misleading and results in progesterone remaining in a constant stimulation mode, perpetuating a state of estrogen dominance. In cases of severe symptoms, such as significant, ongoing bleeding or intense hot flashes, a dosage of up to 400 mg per day may be necessary. It’s important to use no less than 100 mg (or 3 ml) of progesterone. Be sure to apply progesterone at least twice daily, as levels begin to decline after 12 hours.
Normally, men can gain advantages from using 10-20 mg per day of progesterone; however, if there is an elevated level of estrogen, it is recommended to increase the dosage to as much as 100 mg per day.
Once your symptoms have improved and you feel stable, it is fairly straightforward to lower your progesterone levels to better suit your needs. This reduction should always be carried out gradually over the course of several weeks. For guidance on the correct method of reduction, please read First Time Users.
If you have any questions about Natpro Progesterone Cream
It's important to remember that stress can significantly reduce progesterone levels, potentially causing symptoms to re-emerge. If this occurs, consider increasing the cream dosage until you navigate through the stressful period, and then gradually lower it again. Additionally, consuming large meals can also result in lowered progesterone levels due to an accelerated clearance rate of the hormone.
Dark, dreary days and the winter season can lower progesterone levels due to a decrease in vitamin D3. It’s essential to have your vitamin D3 levels tested, as insufficient amounts diminish the effectiveness of progesterone—this is crucial!
Supplemental estrogen can initially make us feel better. The reason for this is estrogen activates the progesterone receptors so making progesterone the dominant hormone, but it wears off as estrogen becomes the dominant hormone. This is one of the reasons so many women keep changing their HRT script. There are some women who do not suffer any adverse effects, but the risks of using HRT or the contraceptive pill for any length of time are not worth it. Please read HRT and Contraceptives.
Estrogen dominance is characterized by any of the following symptoms. These symptoms can also occur in women when first using progesterone. In men too, aside from the obvious women's problems...
- aches and pains
- anger
- anxiety
- bleeding which comes either earlier or later than usual
- bloating/weight gain due to water retention
- breast tenderness
- bruising
- constipation
- dizziness
- headaches
- foggy brain
- heart palpitations/racing heart - see here.
- chest pains/tight chest
- hot flushes
- hypoglycaemia
- dry eyes/sjogren's syndrome
- increased appetite/cravings
- irritation
- itchiness
- migraines
- mild depression
- mood swings
- muscle weakness
- nausea
- skin problems/acne/melasma
- spotting
- tiredness/chronic fatigue
- weight gain/water retention
If you experience any of these symptoms then your choice is to either...
- increase the dose and persevere with the symptoms, or
- reduce the dose considerably to begin with and then gradually increase it over a month or two. This will understandably take longer to resolve symptoms
The Pill and HRT contain estrogen and synthetic progesterone, which is commonly called 'progestin'. Progestins are synthetic and cause natural progesterone levels to drop, leading to many of the above symptoms.
If you are on either HRT or a contraceptive pill and you wish to come off it, it's far gentler on the body to do this gradually in conjunction with progesterone.
Avoid...
- large meals (due to the increased metabolic clearance rate of progesterone)
- all forms of estrogen
- oxidised fats, (ie margarine, refined oils, and fried foods, in particular fried animal protein)
- pasteurised, homogenised milk
- tap water, which is now contaminated with prescription drugs, including estrogen from the Pill and HRT, plus the estrogen mimics generated by industry. Drink only filtered water
If you are considering having your estrogen level tested please ask them to test all 3 levels if possible. Many doctors and labs tend to only focus on the E2 which strictly speaking is incorrect.
- E1 - Estrone
- E2 - Estradiol
- E3 - Estriol
E2 is the most significant of the three estrogens, commonly found in contraceptive pills and hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Additionally, environmental toxins play a role in raising our E2 levels. During peri-menopause and menopause, E2 levels tend to drop. It's also wise to test your progesterone levels to gain a comprehensive understanding of your hormonal balance. There have been reports of some pathologists being unfamiliar with E1 and E3 when it comes to testing. It’s essential to advocate for these tests, as they are two crucial hormones that require assessment. Be aware that some pathologists might not even include them on their testing charts—so make sure to press the issue!
The most effective method of testing is through hair analysis, although it tends to be quite expensive. Saliva testing is also highly reliable, followed by blood tests.
The function of the 3 Estrogens
Estrone (E1)
- also spelled oestrone, is a serioid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol (E2) and estriol (E3). Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized from cholesterol and secreted mainly from the gonads, though they can also be formed from adrenal androgens in adipose tissue. Relative to estradiol, both estrone and estriol have far weaker activity as estrogens. Previously, estrone was available as an injected estrogen for medical use, but it is now no longer marketed. This should be tested when in menopause, it rarely is.
Estradiol (E2) - also spelled oestradiol, is a steroid, an estrogen, and the primary female sex hormone. It is named for and is important in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is essential for the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues such as the breasts, uterus, and vagina during puberty, adulthood, and pregnancy, but it also has important effects in many other tissues, including bone, fat, skin, liver, and the brain. While estrogen levels in men are lower compared to those in women, estrogens have essential functions in men, as well. It is found in most vertebrates and crustaceans, insects, fish, and other animal species.
Estradiol is produced especially within the follicles of the female ovaries, but also in other endocrine (i.e., hormone-producing) and nonendocrine tissues (e.g., including fat, liver, adrenal, breast, and neural tissues). Estradiol is biosynthesized from cholesterol through a series of chemical intermediates. One principal pathway involves the generation of androstenedione, which is converted into estrone by aromatase and then by 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase into estradiol. Alternatively, androstenedione can be converted into testosterone, an androgen and the primary male sex hormone, which in turn can be aromatized into estradiol. Estradiol in a menopausal woman is low, it should be low! It's the pre-menopause estrogen, only made by the ovaries. Once these stop functioning, estradiol diminishes. But, and it's a big but, our fat cells continue making estrone till we die, this is never tested for. It's the menopause estrogen, and it as potent a mitogen as estradiol. Make sure to test Estrone when in peri-menopause and menopause.
Estriol (E3) - also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens. Although it is less commonly used than other estrogens, estriol is available for medical use throughout the world in a variety of formulations, including for oral and vaginal administration.
How to wean off HRT, Estrogen, Progestin, and Testosterone Drugs
It is generally considered safe to discontinue HRT abruptly, unlike many other medications; however, withdrawal symptoms may reappear. A more gentle approach is to gradually taper off HRT while consistently using Natpro Progesterone Cream. Following this method, progesterone typically mitigates any withdrawal symptoms. It is advisable to apply the progesterone cream for a minimum of one month prior to reducing the HRT dosage. For optimal results, use between 100mg/3ml and 200mg/6ml of Natpro daily without interruption—there's no need for a break. If HRT has been in use for an extended period, a higher dose may be necessary. Should symptoms return during the tapering process, increase the progesterone dosage and slow the reduction of HRT.
Follow the instructions below when reducing your dose of HRT, Estrogen or Progestin
- Miss 1 day
- Take 7 days
- Miss 1 day
- Take 6 days
- Miss 1 day
- Take 5 days
- Miss 1 day
- Take 4 days
- Miss 1 day
- Take 3 days
- Miss 1 day
- Take 2 days
- Miss 1 day
- Take 1 day
You have now reduced the dose to 50% over 34 days. Continue missing alternate days until you feel stable, then work back up the list above.
i.e.
Miss 2 days
Take 1 day
Miss 3 days
Take 1 day etc
This may take approximately three months. If you experience no returning symptoms and feel stable, you may stop the HRT, etc.
VITAMIN D3 – I cannot emphasize enough how essential it is! Please ensure you have your vitamin D3 levels checked and visit the vitamin D3 page for additional information. Among numerous other health concerns, it aids in combating depression, insomnia, MS, cancer, and infertility—the list goes on and on.

